
矿热炉在使用中产生大量的谐波,导致电网中的谐波污染非常严重。矿热炉一般由可控硅整流装置提供直流电源。可控硅整流装置会在交流侧产生很大的无功功率和谐波电流,导致电压、电流波形严重畸变,功率因数低,造成进线电流大,变压器利用率降低,能耗增加。谐波还会干扰拉晶控制系统,造成错位、断晶、跳闸,严重影响正常生产。 矿热炉是一种高能耗的电冶炼炉,具有电阻电弧炉的特性。其功率因数是由炉内电弧及电阻R和电源回路中(包括变压器、短网、集电环及电极)的电阻R和电抗X值的大小来决定。 COSΦ=(R+R)/ 电阻R电抗X值在矿热炉运行时,一般不变动,它们取决于短网和电极布置的设计和安装。电阻R与运行时短网上各载流部件的电流密度有关,变化较小,但电阻R却是矿热炉运行时决定矿热炉功率因数的主要因数。 由于矿热炉比其它电冶炼炉的电阻弱,故其功率因数相应地也降低些。除了一般小型矿热炉的自然功率因数能达到0.9以上,而容量在10000KVA以上的中、大型矿热炉的自然功率因数都在0.9以下,矿热炉容量越大,功率因数越低。这是由于大容量矿热炉的变压器感性负载越大,短网越长,电极[敏感词]炉料较深增加了短网的电抗,因而降低了矿热炉的功率因数。 为了减少电网的损耗,提高供电质量,供电局要求用电企业的功率因数要在0.9以上,否则要对用电企业处以高额罚款。同时功率因数偏低,也会降低矿热炉的进线电压,影响电石的冶炼。故目前国内外大容量矿热炉都要加装无功补偿装置,以提高矿热炉的功率因数。
现在投运的无功补偿装置通常以补偿装置的接入点分为下列两种方式:
1、补偿装置接入矿热炉变压器高压侧,称高压补偿;
2、补偿装置接入矿热炉变压器低压侧,称低压补偿;
二、无功补偿装置
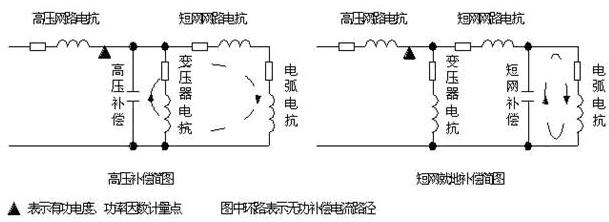
1、高压补偿
矿热炉变压器高压侧电压一般为10KV、35KV、或110KV。高压补偿又分两种:一种是直接将补偿装置接于高压侧;另一种是通过补偿变压器接于高压侧。用相应电压等级的补偿装置(包括电力电容器、开关、电抗器、避雷器、保护等成套设备,下同),直接接入矿热炉变压器高压侧(补偿装置接在矿热炉变压器进线端),也可以直接在变电站中,单独或集中补偿。其特点是:
1)设备简单,投资少;
2)补偿装置出现故障时电流不通过矿热炉变压器;
3)补偿装置不受矿热炉变压器接线变换及矿热炉其它方面变化的影响。
2、低压补偿
2.1原理
低压补偿是利用现代控制技术和短网技术将大容量、大电流的超低压电力电容接入矿热炉的二次侧的无功补偿装置。该装置不仅是无功功率补偿原理的好体现,还可以使矿热炉的功率因数在较高值运行,降低短网和一次侧的无功消耗,消除3次、5次、7次谐波。调平三相功率,提高变压器的输出能力。控制的重点使三相功率不平衡度下降,达到三相功率相等。使坩锅扩大、热量集中,提高炉面温度,使反应加快,达到提高产品质量、降耗和增产的目的。
此技术属于将原来成熟的就地补偿技术应用到矿热炉的二次低压侧,由电容器产生的无功功率,通过短线路,一部分通过矿热炉变压器由系统吸收,另一部分补偿矿热炉变压器,短网和电极的无功损失,增加了输入矿热炉的有功功率。同时采用了分相补偿,使矿热炉内三相电极上的有功功率相等,达到提高功率因数,减小三相功率不平衡和改善生产指标的效果。采用低压就地补偿/滤波技术优点:
1、低压补偿可以提高变压器、大电流线路利用率,增加冶炼有效输入,
2、改善三相不平衡。
3、降低高次谐波值。
4、减小变压器及网路附加损耗,可以消除力调电费,节能降耗。
5、提高矿热炉变压器有功出力,从而提高产量,增加经济效益。
The reactive power compensation devices currently in operation are usually divided into the following two ways based on the access point of the compensation device:
1. The compensation device is connected to the high voltage side of the ore furnace transformer, which is called high voltage compensation;
2. The compensation device is connected to the low voltage side of the ore furnace transformer, which is called low voltage compensation;
2、 Reactive power compensation device

1. High voltage compensation
The high voltage side voltage of the ore furnace transformer is generally 10KV, 35KV, or 110KV. There are two types of high-voltage compensation: one is to directly connect the compensation device to the high-voltage side; Another way is to connect it to the high voltage side through a compensating transformer. Compensation devices with corresponding voltage levels (including power capacitors, switches, reactors, lightning arresters, protection equipment, etc., the same below) can be directly connected to the high voltage side of the submerged arc furnace transformer (the compensation device is connected to the input end of the submerged arc furnace transformer), or directly compensated separately or centrally in the substation. Its characteristics are:
1) Simple equipment and low investment;
2) When the compensation device malfunctions, the current does not pass through the ore furnace transformer;
3) The compensation device is not affected by changes in the wiring of the ore furnace transformer or other aspects of the ore furnace.
2. Low voltage compensation
2.1 Principle
Low voltage compensation is a reactive power compensation device that uses modern control technology and short network technology to connect large capacity and high current ultra-low voltage power capacitors to the secondary side of a submerged arc furnace. This device not only embodies the principle of reactive power compensation, but also enables the power factor of the ore blast furnace to operate at a higher value, reducing the reactive power consumption of the short network and primary side, and eliminating the 3rd, 5th, and 7th harmonics. Leveling the three-phase power and improving the output capacity of the transformer. The focus of control is to reduce the imbalance of three-phase power and achieve equal three-phase power. Expand the crucible, concentrate heat, increase the furnace surface temperature, accelerate the reaction, and achieve the goal of improving product quality, reducing consumption, and increasing production.
This technology belongs to the application of mature on-site compensation technology to the secondary low voltage side of the submerged arc furnace. The reactive power generated by capacitors is absorbed by the system through a short line, partially through the submerged arc furnace transformer, and partially compensates for the reactive power loss of the submerged arc furnace transformer, short network, and electrodes, increasing the active power input to the submerged arc furnace. At the same time, phase separation compensation is adopted to make the active power on the three-phase electrodes in the ore blast furnace equal, achieving the effect of improving power factor, reducing three-phase power imbalance, and improving production indicators. Advantages of using low-voltage on-site compensation/filtering technology:
1. Low voltage compensation can improve the utilization rate of transformers and high current lines, increase the effective input of smelting,
2. Improve three-phase imbalance.
3. Reduce high-order harmonic values.
4. Reducing transformer and network additional losses can eliminate power regulation electricity costs and save energy and reduce consumption.
5. Improve the active power output of the ore smelting furnace transformer, thereby increasing production and economic benefits.